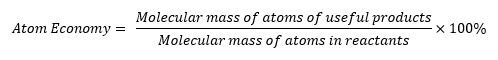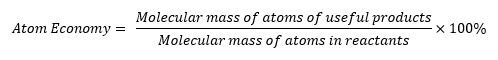Skip to content
Home 1.1 Introduction to the particulate nature of matter and chemical change
1.1 Introduction to the particulate nature of matter and chemical change
States of matter
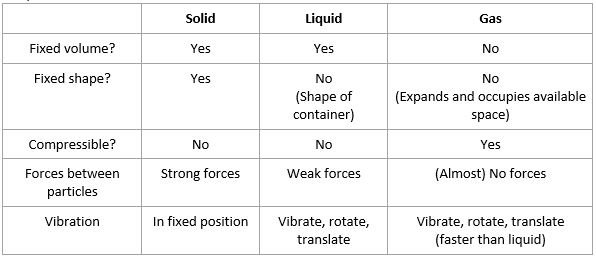
- Everything is made up of matter. The characteristics of matter are:
- Made up of particles – atoms, molecules or ions
- Particles are in constant motion
- Occupies a volume in space
- Has a mass
Properties of three states of matter
Temperature
- The vibration and movement of particles depend on temperature
- As temperature increases, KEavg increases
- The SI unit for temperature is the kelvin (K)
- Absolute zero is 0 on the kelvin scale (-273° on Celsius scale), and is the temperature at which all movement of particles stops
- Temperature (K) = Temperature (°C) + 273.15
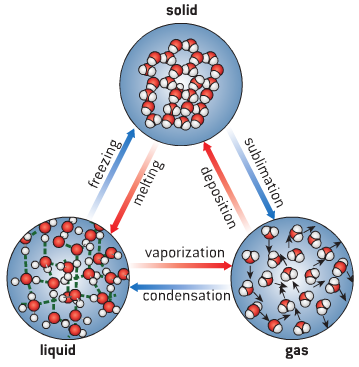
Changes of State
- Take water for example:
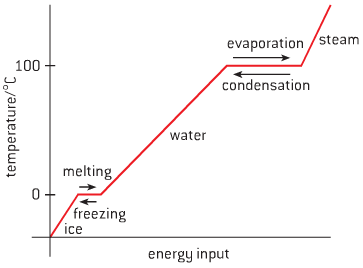
- As temperature increases, kinetic energy in particles increase, causing change of state
- Melting and boiling are endothermic reactions – energy is transferred from environment
- As temperature decreases, kinetic energy decreases, causing reversal of state
- Condensation and freezing are exothermic reactions – energy is transferred to environment
- There is no change in temperature while melting, boiling, condensing or freezing,
- energy is used to break/create attractive forces so change of state can occur
- Changes of state can be described using the following terms:
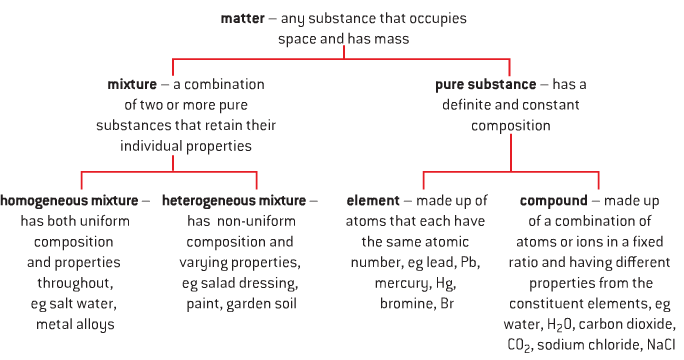
Classification of Matter
- Ion: A charged species
- Anion: Negatively charged ion
- Cation: Positively charged ion
How to balance equations
4 types of chemical reactions
- Synthesis
- Decomposition
- Single Displacement
- Double Displacement
- Complete Combustion
- Incomplete Combustion
State symbols
- (s) – solid
- (l) – liquid
- (g) – gas
- (aq) – aqueous
The Atom Economy
- Is a measure of the amount of starting materials that become useful products.
- High atom economy means that less waste is created and reaction has a high efficiency