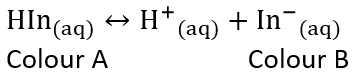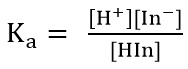18.3 pH curves
Buffer solutions
- A buffer is a solution that resists a change in pH upon addition of small amounts of a strong base, strong acid or water.
- Buffer Is composed of weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid
Indicators
- An acid-base indicator is a weak acid or a weak base where the componets of the conjugate acid-base pair have different colours
- When choosing the best indicator for a titration, the midpoint of an indicators colour change must correspond to the equivalent point of the titration
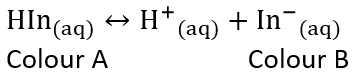
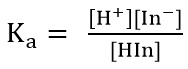
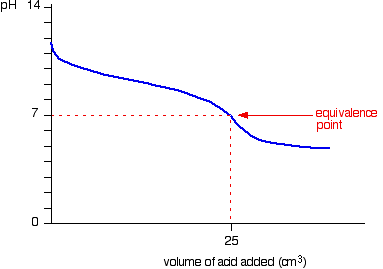
pH curves
- There are 4 possibilites of pH curves
- Strong acid – Strong base
- Starting point on pH axis is important as it gives initial pH of acid
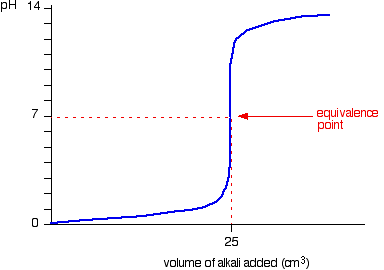
- Weak acid – Strong base
- Starting point on pH axis is important as it gives initial pH of acid
- Half equivalence point is the stage at which half the amount of weak acid has been neutralized
- At this point, pKa=pH
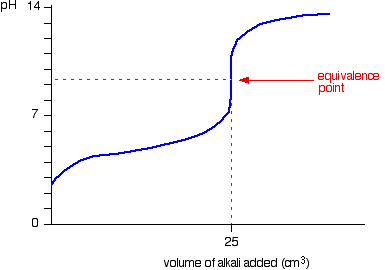
- Strong acid – Weak base
- Starting point on pH axis is important as it gives initial pH of base
- Half equivalence point is the stage at which half the amount of weak base has been neutralized
- At this point, pKb = pOH
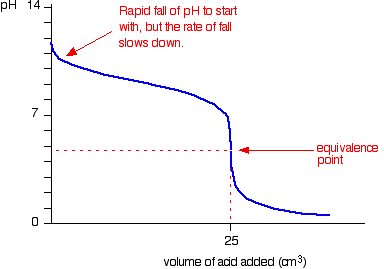
- Weak acid – Weak base
- Starting point on pH axis is important as it gives initial pH of base
- Gradual change, equivalence point is hard to determine, graph has no purpose