Home 4.2 Covalent bonding
4.2 Covalent bonding
Covalent Bonding
- Formed by electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the positive nuclei
- In ionic, atoms lose or gain electrons. In covalent, atoms share electrons to achieve noble gas configuration
- Occurs between non-metals
- There are single bonds (F2), double bonds (O2) and triple bonds (N2)
- There is also HF for example in which H does not acquire a octet rule
Bond Strength and bond Length
- The trend in bond strength is:
- The trend in bond length is
Electronegativity
- Electronegativity is the relative attraction that an atom of an element has for the shared pair of electrons in covalent bond.
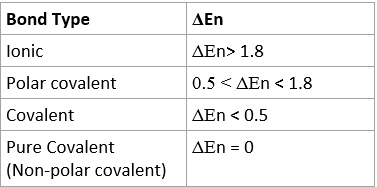
- It can be determined with electronegativity values the type of bond:
- To find Δen, subtract the electronegativity values for two atoms