Home 11.1 Uncertainties and errors in measurements and results
11.1 Uncertainties and errors in measurements and results
Qualitative & Quantitative Analysis
- Analysis of data can be classified into two types
- Qualitative Analysis
- Comes from observations and non-numerical methods
- Quantitative Analysis
- Comes from measurements and always associated with uncertainties determined by either the apparatus and human limitations such as reaction times and sight
Uncertainties
- In science, numerical data is divided into two types
- Data with exact numbers (no uncertainty)
- Data with inexact numbers (Degree of uncertainty involved)
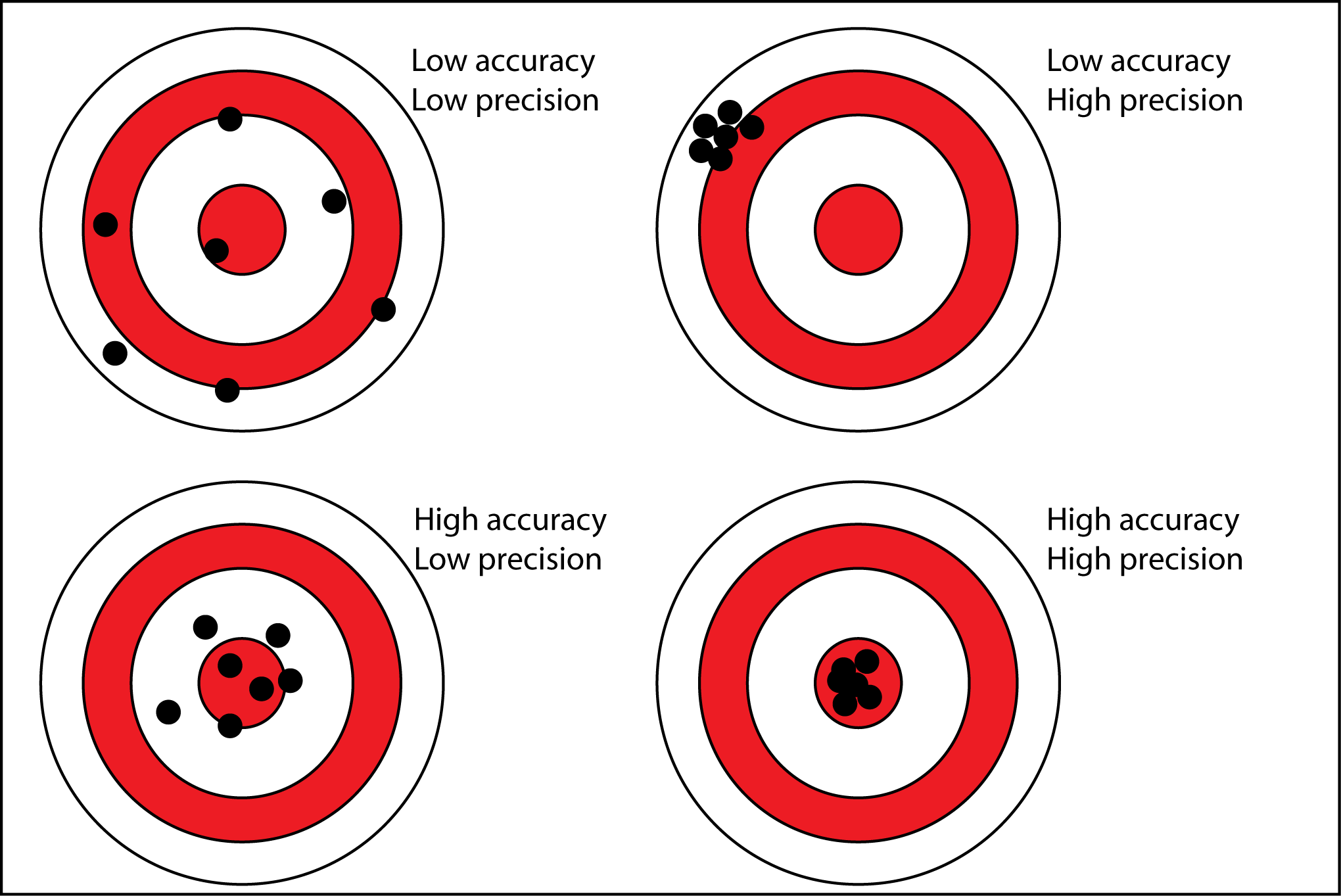
Precision vs Accuracy
- Precision: Closeness of agreement between interdependent test results
- Accuracy: Closeness of agreement between the result of measurement and the true value
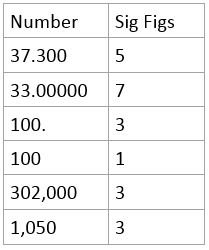
Significant Figures
- Number of digits reflecting precision of a given measurement
- Sometimes it is useful to write in Scientific notation
- Here are some examples:
- Some rules for significant figures in calculation
- For multiplication or division: Result should be expressed based on measurement with smallest number of significant figures.
- For addition or subtraction: Result should be expressed based on measurement with smallest number of decimal places
- (A simple rule on the side is that your final answer should be expressed in the number of significant figures of the measurement with the lowest number of significant figures)
Experimental Error
- Every measurement has a degree of uncertainty with it called experimental error
- There are two types of experimental error
- Systematic error: A flaw in experimental design or methodology. This affects the accuracy of the results.
- Random error: Occur because of uncontrolled variables. Cannot be eliminated. This affects the precision of the results.
Absolute and Relative Uncertainty
- Absolute Uncertainty is the margin of uncertainty associated with the result from a measurement.
- Its symbol is given by ΔA
- Relative Uncertainty is the ratio comparing the size of the absolute uncertainty.
- Relative uncertainty = ΔA / A
- All experimental results should be reported in form:
- Experimental result = (A ± ΔA) units
Percentage Error


