Skip to content
Home 1.2 The mole concept
1.2 The mole concept
- Particles are classified as either: Atoms, ions, molecules or formula units
- To perform chemistry, moles of substance are used, and this allows us to make comparisons between chemical species.
The Mole
- Avogadro’s constant NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
- Mole: a fixed number of particles and refers to the amount, n, of substance
- Molar mass: mass of 1 mole of a substance (g mol-1)
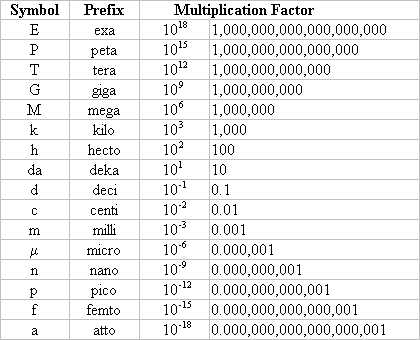
- Number prefixes which are important to know:
Mole Calculations

Relative atomic mass & molar mass
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element which have same number of protons
- Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers
- Relative abundance: Measure of percentage of isotopes present in element
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): weighted average of the atomic masses of its isotopes and their relative abundances
- Relative because compared to 1 atom of carbon-12 (12C) which is 12 units
- Relative molecular mass (Mr): Combining individuals Ar values of atoms in molecule or formula unit
Empirical and molecular formula determination
- Empirical formula: simplest whole number ratio of atoms or amount (in mol) of each element present in a compound
- Molecular Formula: the actual number of atoms or amount (in mol) of elements in one structural unit or one mole of the compound


