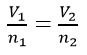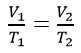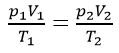Stoichiometry
- Stoichiometry is the quantitative method of examining the relative amounts of reactants and products
The limiting reagent
- Limiting reagent is completely consumed during a reaction, the remaining reactants are in excess
- The limiting reagent is what is used to determine the amount of products formed
Percentage Yield
- Percentage yield is used to determine the efficiency of a reaction
- Some factors for where yield is lost include:
- Loss of products from reaction vessels
- Impurity of reactants
- Changes in reaction conditions, such as temperature and pressure
- Reverse reactions consuming products in equilibrium systems
- Existence of side reactions due to impurities
Molar volume of a gas
- Ideal gas is a gas which follows the kinetic theory of gases. They are found in systems with high temperature and low pressure.
- Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP): The conditions where temperature is 273K and pressure is 100 kPa.
- At STP, the Molar Volume of an ideal gas is 22.7 dm3 mol-1
- Avogadro’s Law: Equal volumes of any gas measured at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules
The Gas Laws
Molar Concentration
Titrations
- Titration involves a standard solution of known concentration which is added to a solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction is complete
- Watch this video