- Alkanes
- Combustion
- Alkanes undergo complete combustion in presence of excess oxygen
- Alkanes undergo incomplete combustion in limited supply of oxygen (producing carbon monoxide or even just carbon atoms)
- Halogenation (Substitution and elimination. Free radical substitution)
- Alkanes undergo free–radical substitution and elimination to form unsaturated alkenes and alkynes
- Free-Radical substitution
- Occurs in presence of UV light
- Free-radical refers to species formed when molecule undergoes homolytic fission
- Homolytic fission: The two electrons of a covalent bond are split evenly between two atoms resulting in two free-radicals that each have a single electron
- Heterolytic fission: The bond creates a cation and an anion because the electrons are unevenly split (both electrons go to one atom)
- There are three steps involved in free-radical substitution reaction between methane and chlorine:
- Initiation: The homolytic fission of the chlorine molecule in the presence of UV light.
- Propagation: The radicals react with neutral atoms in attempt to gain stability. The target neutral atom then becomes a radical in the process.
- Termination: Radicals join together creating new compounds in the process. This occurs either when:
- Emission of UV light is stopped preventing creation of radicals
- Concentration of hydrocarbons decrease because they “mop up” the radicals
- Combustion
- Alkenes
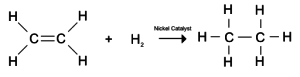
- Hydrogenation
-
- Alkenes undergo addition reactions
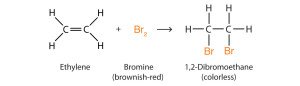
- A mixture of alkene and bromine water will undergo a colour change from brown to colourless. This indicates the presence of unsaturated molecules
-
- Halogenation
- Electrophilic halogenation of symmetrical alkenes involves addition of elemental halogens resulting in dihalogenated alkane
- Addition of hydrogen halide (HX) to a symmetrical alkene results in single mono-halogenated alkane
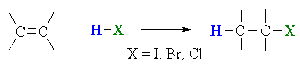
- (Addition to Asymmetrical alkenes is covered in topic 20.1)
- Electrophilic halogenation of symmetrical alkenes involves addition of elemental halogens resulting in dihalogenated alkane
- Polymerization
- Addition polymerization is the reaction of many small monomers that contain carbon-carbon double bond, linking together forming a polymer
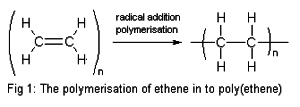
- Addition polymerization is the reaction of many small monomers that contain carbon-carbon double bond, linking together forming a polymer
- Hydrogenation
- Alcohols
- Can undergo complete combustion releasing CO2 and H2O
- Oxidation
- Oxidation of primary alcohols is a two step process
- The oxygen donor [O] is normally acidified K2Cr2O7
- Primary Alcohols:
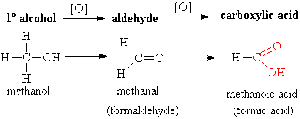
- Secondary Alcohols:
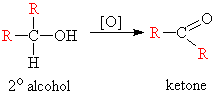
- Condensation
- Between alcohol and carboxylic acid
- The catalyst used is normally H2SO4
- Esterification is a reversible process
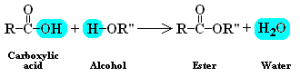
- Between alcohol and carboxylic acid
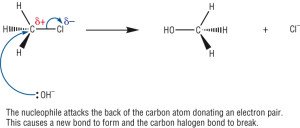
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- Halogenoalkanes contain a polar carbon – halogen bond (C-X)
- This electron deficient carbon is open to attack by electron rich species known as nucleophiles
- Nucleophile contain a lone pair of electrons and sometimes have a full negative charge
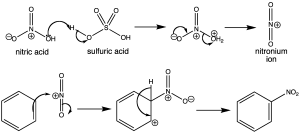
Electrophilic Substitution
- Used for aromatic or compounds with double/triple bonds
- Benzene does not readily undergo addition reactions. Instead, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions.
- Electrophile is an electron poor species capable of accepting an electron pair
- Arrows show movement of electrons