15.1 Energy cycles
- Born-Haber cycle is an application of Hess’s Law, and is a series of reactions that can be combined to determine the enthalpy of formation of an ionic compound.
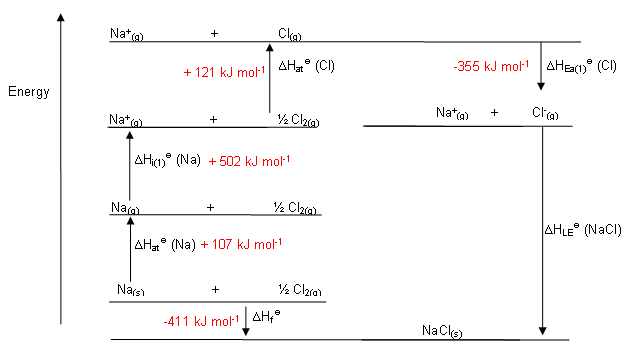
Making a Born-Haber Cycle
- Lattice enthalpy: The standard enthalpy change that occurs on the formation of 1 mol of gaseous ions from the solid lattice. The symbol is ΔHѳlat
- Enthalpy of atomization: The standard enthalpy change that occurs in the formation of 1 mol of separate gaseous atoms of an element in standard state. ΔHѳat
- Ionization energy: The standard enthalpy change that occurs on the removal of 1 mol of electrons from 1 mol of atoms or positively charged ions in gaseous phase. ΔHIE
- Electron affinity: The standard enthalpy change in the addition of 1 mol of electrons to 1 mol of atoms in the gaseous phase. ΔHѳEA
Enthalpy changes in solution
- Enthalpy of solution: The standard enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mol of a substance is dissolved in a large excess of a pure solvent. The symbol is ΔHѳsol
- Enthalpy of hydration: The standard enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mol of a gaseous ion is added to water to form a dilute solution. Solvation is used instead of hydration if the solvent is not water. The symbol is Δhѳhyd
Variations in lattice and hydration Enthalpy Values
- Magnitude of enthalpy for ionic compound is affected by both charge and ionic radii of atoms
- Increase in ionic charge results in increase of enthalpy
- Increase in ionic radii results in decrease of enthalpy

