Skip to content
Home 18.1 Lewis acids and bases
18.1 Lewis acids and bases
Defining Lewis acids and bases
- Bronsted-Lowry base is defined as substance which accepts proton. The presence of a lone pair of electrons is what allows a Bronsted-Lowry base to form a coordinate bond with a proton
- Lewis acid is electron pair acceptor, Lewis base is electron pair donor
- Lewis theory is more general and applicable to more substances
Forming coordinate bonds
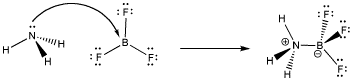
- Take reaction between boron trifluoride and ammonia
- Ammonia donates a lone pair of electron to form coordinate bond
- Boron forms three hybridized sp2 hybrid orbitals resulting in a vacant unhybridized 2pz orbital
- Lone pair from nitrogen fills 2pz orbital
- Transition elements have a partially occupied d subshell so they form complex ions with ligands that possess a lone pair of electrons
- Metal atom or ion acts as Lewis acid, ligand as Lewis base. Example:
- H2O, NH3, Cl–, CN– and OH– act as Lewis bases in forming complexes
- Lewis bases are also nucelophiles
- Lewis acids are electrophiles