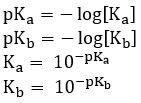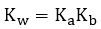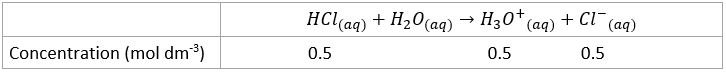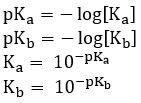Home 18.2 Calculations involving acids and bases
18.2 Calculations involving acids and bases
The strengths of acids and the acid dissociation constant
- Strong acids and bases:
- Since strong acids are assumed to completely dissociate in water, the concentration of each of the two ions produced is the same as the initial concentration of a strong monoprotic acid (one hydrogen)
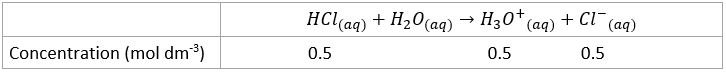
- Weak acids and bases:
- Since these do not complete dissociate, the concentration of products is not the same
- The way to solve for concentrations is using the equilibrium expression
- Acid dissociation constant:
- Base dissociation constant:
Calculating Ka and Kb
- Write out the complete reaction
- Complete an ICE table
- Determine Ka or Kb
Ka and Kb for a conjugate acid-base pair
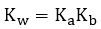
- Strong acid
- Large Ka
- Weaker conjugate base
- Smaller Kb of conjugate base
- Strong base
- Large Kb
- Weaker conjugate acid
- Smaller Ka of conjugate acid
The temperature dependence of Kw
- Kw is defined only at 25°C
- The ionization of water is endothermic, so as temperature increases, equilibrium shifts right
- Increase in concentration of H+ results in decrease in pH
pKa and pKb
- The pH scale can be applied to Ka and Kb to get pKa and pKb