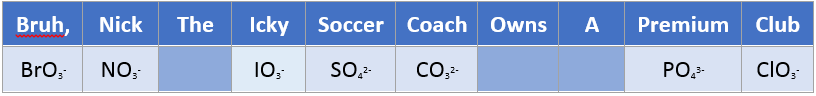Ionic Bonding
- Ionic Bond is due to electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
- Ions are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
- The number of electrons lost or gained is determined by the electron configuration of the atom
- The reason there is transfer of electrons is because they want to achieve a noble gas configuration
- Positive ions (Cations) form by metals losing valence electrons
- Negative Ions (Anions) form by non-metals gaining electrons
- OIL RIG
- Oxidation Is Loss of electrons
- Reduction Is Gain of electrons
- Ionic compounds are typically solids and have lattice-type structures that consist of 3D repeating units of positive and negative ions
- OIL RIG
Oxyanions
Easy way to memorize all the oxyanions is to remember the following sentence, and the rules to go with them.
- Consonants are the number of oxygens, vowels is the charge.
Let’s take premium (PO43-) for example:
- Premium there are 3 vowels. Thus the charge is 3-
- Premium there are 4 consonants, thus there are 4 oxygen’s
- PO43-
Physical Properties
- Volatility
- Tendency to vaporize. Ionic compounds have strong electrostatic forces thus they have low volatility
- Electrical Conductivity
- For ionic compound in solid state, ions occupy fixed position. Hence, they do not move around or conduct electricity. In molten state they are free to do so.
- Solubility
- Ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents such as water
- This is because partial charges of polar solvents are attracted to ions in the lattice
- As result, individual ions are pulled out of lattice structure