Skip to content
5.3 Bond enthalpies
Bond Enthalpy
- Bond (dissociation) Enthalpy: The energy required to break 1 mol of bonds in gaseous covalent molecules under standard conditions
- Bond breaking is endothermic process and has a positive enthalpy value
- Average values found in section 11 of the data booklet
- Bond length
- As atomic radius increases, so does bond length. This results in decrease on bond strength
- Bond Strength
- Bond enthalpy reflects strength of covalent bond
- As number of bonds increase (single, double, triple), the bond strength increases, and bond length decreases
- Bond Polarity
- Determined by difference in electronegativity
Ozone
- Ozone, O3 is created and destroyed in stratosphere. UV rays split O2 molecules into single oxygen atoms, then these radicals combine with oxygen molecules to create ozone.
- The importance of ozone is that it is very effective at blocking harmful long and short wavelength UV radiation. Without ozone, radiation would harmfully damage cells on plants and animals.
- Ozone molecule is decomposed more readily than oxygen molecule because it is at higher energy state and less stable
Calculations
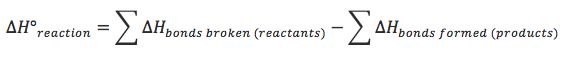
- Note: The answer calculated will vary from actual answer since the bond enthalpy values are an average, and this does not take into account intermolecular forces which are broken as well

