Skip to content
Home 8.1 Theory of acids and bases
8.1 Theory of acids and bases
The role of acids and bases
- Acids and bases are opposites
- Many theories describe how they work
- Arrhenius Theory of acids and bases
- Acids produce H+ ions, bases produce OH– ions
- Neutralization is the process of combining an acid and a base
- Limitation: weak base ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas could not be explained, as ammonia does not contain OH–
- Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases
- Refer to hydrogen ion as a proton;
- Acid is proton donor, base is proton acceptor
Conjugate acids and bases
- In a reversible reaction between acid and bases, there are conjugates as well

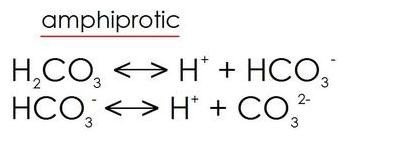
Amphiprotic species
- Amphiprotic species: Substances which can be both Bronsted-Lowry acids or bases depending on the reaction