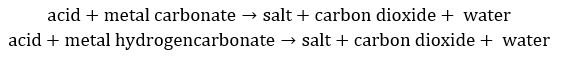Home 8.2 Properties of acids and bases
8.2 Properties of acids and bases
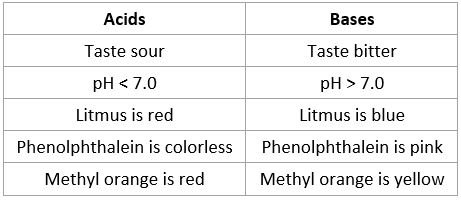
Properties of acids and bases
Reactions of acids with metals, bases, and carbonates
- Most acids react with metals, metal oxides, hydroxides, hydrogencarbonates and carbonates
- All these reactions produce a salt which is a compound of anion and cation
- Standard enthalpy change of neutralization: the energy change associate with the formation of 1 mol of water from the reaction between a strong acid and a strong base under standard conditions
- Negative value because neutralization is exothermic
- For acids and bases:
- For metals higher than hydrogen on activities series:
- For metal carbonates and hydrogencarbonates:
Acid-Base titrations
- Refer to section 22 of data booklet to see colour changes associate with indicators