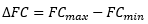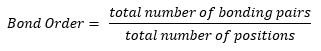Home 14.1 Covalent bonding and electron domain and molecular geometrics
14.1 Covalent bonding and electron domain and molecular geometrics
Formal Charge
- Sometimes there are multiple ways of drawing Lewis structures that obey the octet rule, best one can be determined by the hypothetical formal charge equation
- FC = V – N – 1/2B
- Where V is number of valence electrons
- N is number of non-bonding electrons
- B is number of bonded electrons
- The correct Lewis structure of a molecule can be determined by:
- When it is closest to 0
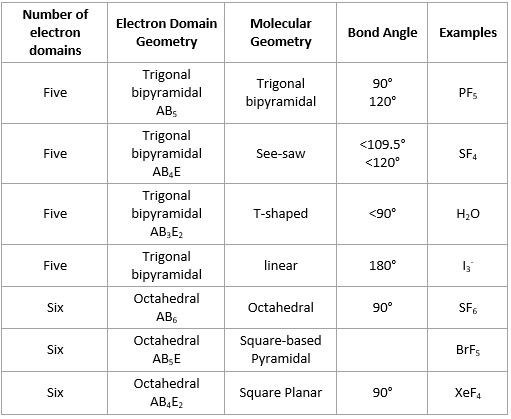
Molecular Geometries based on five and six electron domains
Overlap of atomic orbitals: Sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonding
- Single covalent bond sharing 2 electrons is a sigma bond (σ)
- Double covalent bond consisting of 4 electrons, 2 pairs, is a sigma plus pi bond (σ + π)
- Triple covalent bond consisting of 6 electrons, 3 pairs, is a sigma plus two pi bonds (σ + 2π)
Delocalization and Resonance
- Two or more different arrangements of electrons
- The actual bond length is between them
- Both Lewis structures are resonance forms and contribute to structure called resonance hybrid
- Dashed curve conveys delocalization
- Delocalization is a quantum mechanical model to describe pi bonding in a conjugated system
- Conjugated System is a molecular entity whose structure can be represented as a system of alternating single and multiple bonds
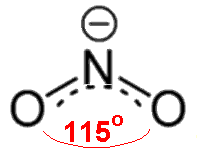
Ozone Depletion
- Ozone is a bent molecule with bond angle 116.8°
- It has a resonance structure
- UV light radiation from the sun is very high in energy and is able to break the oxygen to oxygen bonds in ozone.
- In the stratosphere, ozone absorbs over 95% of UV radiation from sun. It under goes homolytic fission and converts UV radiation to heat.
- Chlorine atoms are produced in the reaction of a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) with UV light. These also undergo homolytic fission and the chlorine radicals attack ozone molecules. Thus depleting the ozone layer.